Wednesday, August 14, 2013
Products Wiring Harnesses Harness1986 Corvette
Rbe Hlt Testers Trailer Vehicle Wiring Harness Tester.
Engine Wiring Diagram 1 How To Wire A Car Engine Prestolite Wire.
Vehicle Wiring Products.
Gm Tpi Products Wiring Harnesses Tpi Harness 1986 89 Corvette.
Other Products Delfingen Industry.
Hydrox Mobile Rus Products Vehicle Wiring Diagram.
Wiring Connections For Gm Serpentine Kit Alternators.
Split Charge Electrical Wiring Diagram.
Our Products Wiring Diagram 1970 76 Tecumseh Powered.
Products Accessory Equipment Light Vehicle Wiring Kit Roll Bar.
Labels:
corvette,
harness1986,
harnesses,
products,
wiring
Sunday, August 11, 2013
Universal Compander Circuit diagram
Signet type NE575 compander IC is intended primarily for use with battery power supplies of 3 to 7 V (max. 8 V). Itdraws a current of 3.5 mA at 3 V and 5 mA at 7 V. The compander process (compression at the input, expansion at the output) significantly improves the signal-to-noise ratio in a communications link.
Universal Compander Circuit diagram
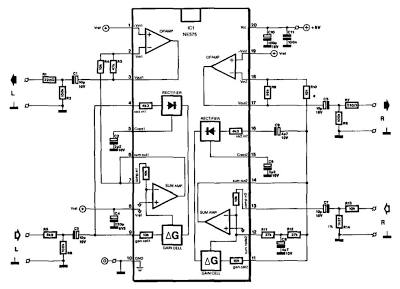
The IC contains two almost identical circuits, of which one (pins 1 to 9) is arranged as an expander. The other (pins 11 to 19) can be used as expander, compressor or automatic load control (ALC), depending on the externally connected circuit. For the compressor function, the inverting output of the internal summing amplifier is brought out to pin 12.
This is not the case in the expander section, where a reference voltage is available at pin 8. This pin is interlinked to pins 1 and 19 to enable the setting of the dc operating point of the op amps. The op amp in the expander section, pins 1 through 3, serves as output buffer in the compressor section, pins 17 through 19 as the input buffer. The IC has a relatively high output sensitivity and is evidently intended for processing small signals (microphone output level).
A signal of 100 mV, for instance, is amplified by 1 only. The present circuit caters to larger input signals (line level); its maximum input level is 1.5 Vrms. With a 1-V input into R13, a potential of about 500 mV exists between compressor output R7 and expander input R5. The compression characteristic is shown in Fig. 19-2 (b). The signal range is reduced by about one half at the output, which is doubled in the expander. Thus, the range after compression and expansion is the same again, but that is not necessarily the case with the input and output level. The compander can be arranged to provide a constant attenuation or amplification. With the circuit values as shown in the diagram, the input and output levels are the same.
The prototype had an overall gain of 0.5 dB when the expander input was connected directly to the compressor output. To allow acceptance of high input levels, R13, R14, and the compressor input resistance form a 10:1 attenuator. At the expander input, R5 and the expander input impedance of about 3 kfl form a potential divider. If the compander is to be used with smaller signals, the attenuation can be reduced as appropriate. If the input level lies below 100 mV, R5, R13 and R14 can be omitted. The compander covers the frequency range of 20 Hz to 20 kHz, the overall distortion is less than 1%, and the signal-to-noise ratio is about 80 dB.
Thursday, August 8, 2013
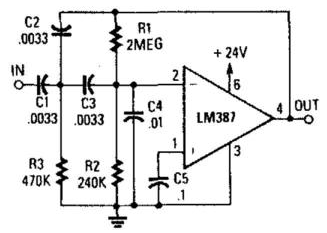
Simple Rumble Filter Circuit Diagram
This simple rumble filter circuit diagram is a two-section active HP filter using an LM387, with a cutoff below 50 Hz at 12-dB per octave. It will help reduce rumble as a result of turntable defects in record systems.
Simple Rumble Filter Circuit Diagram
Monday, August 5, 2013
Mobile Cellphone Battery Charger
Charging of the mobile phone battery is a huge issue while traveling as power supply source is not usually available. In case you keep your mobile phone switched on continuously, its battery will go flat within to six hours, making the mobile phone useless. A fully charged battery becomes necessary when your distance from the nearest relay station increases. Here is a simple charger that replenishes the mobile phone battery within to hours. Fundamentally, the charger is a current-limited voltage source. Usually, mobile phone battery packs need three.6-6V DC & 180-200mA current for charging. These usually contain NiCd cells, each having one.2V rating. Current of 100mA is for charging the mobile phone battery at a slow rate. A 12V battery containing eight pen cells gives sufficient current (one.8A) to charge the battery connected across the output terminals.

Diagram of cellphone charger
The circuit also monitors the voltage level of the battery. It automatically cuts off the charging system when its output terminal voltage increases above the predetermined voltage level. Timer IC NE555 is used to charge & monitor the voltage level in the battery. Control voltage pin five of IC1 is supplied with a reference voltage of five.6V by zen-er diode ZD1. Threshold pin 6 is supplied with a voltage set by VR1 & trigger pin two is supplied with a voltage set by VR2. When the discharged mobile phone battery is connected to the circuit, the voltage given to trigger pin two of IC1 is below 1/3Vcc & hence the flip-flop in the IC is switched on to take output pin three high.

When the battery is fully charged, the output terminal voltage increases the voltage at pin two of IC1 above the trigger point threshold. This switches off the flip-flop & the output goes low to terminate the charging method. Threshold pin 6 of IC1 is referenced at 2/3Vcc set by VR1. Transistor T1 is used to enhance the charging current. Value of R3 is critical in providing the necessary current for charging. With the given value of 39-ohm the charging current is around 180 mA.
The circuit can be constructed on a tiny general-purpose PCB. For calibration of cut-off voltage level, use a variable DC power source. Connect the output terminals of the circuit to the variable power supply set at 7V. Fine-tune VR1 in the middle position & slowly fine-tune VR2 until LED1 goes off, indicating low output. LED1 ought to turn on when the voltage of the variable power supply reduces below 5V. Enclose the circuit in a tiny plastic case & use suitable connector for connecting to the cell phone battery.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)